Slot Conventions¶
For the definition of the slot geometry with build_geometry() the following conventions are used:
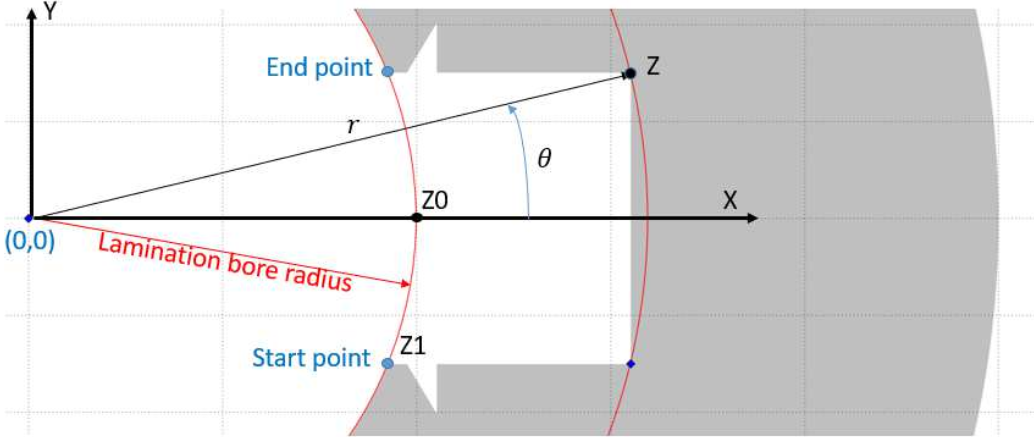
Starting and ending points of the curve defining the slot edges should be on the lamination bore radius.
Line objects are ordered in the trigonometric direction (therefore the imaginary part of the first point is negative and the one of the last point is positive).
All the coordinates are by default returned with the Ox axis as the symmetries axis of the slot (or in the middle of the slot opening if the slot is not symmetrical).
Points are named Px, their complex coordinate is Zx. The arc center points are named Pcx in schematics.
The top of the slot is the closest part to the bore radius, the bottom of the slot is the closest part to the yoke (for both outer and inner rotor).
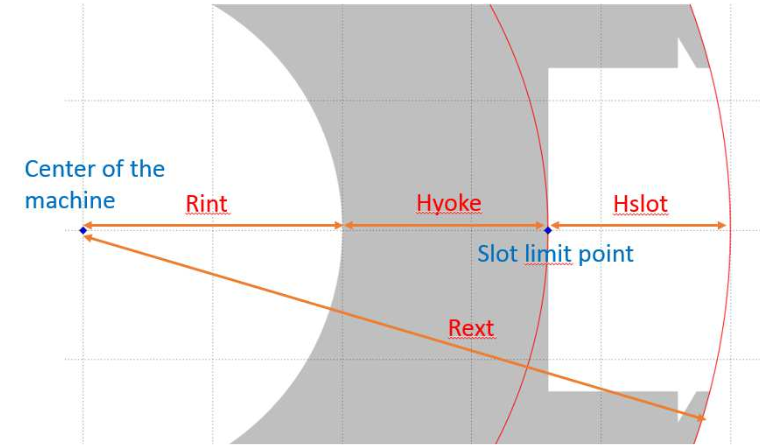
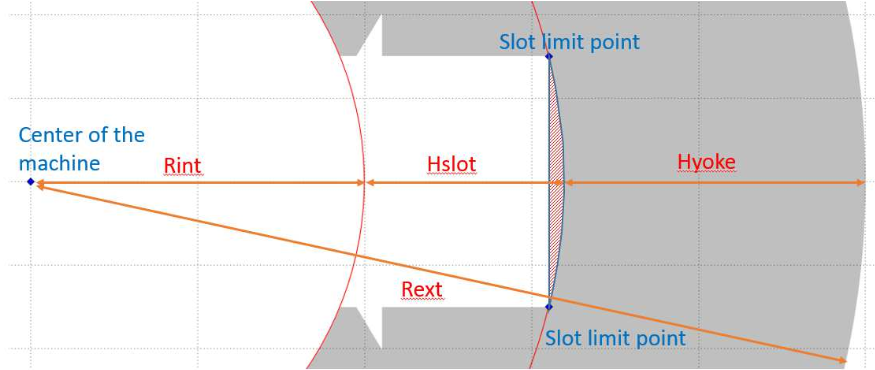
The slot bottom radius is the radius of the point which is the furthest from the bore.
The slot height is defined as the difference between the lamination bore radius and the slot bottom radius.
The top of the slot surface is always defined by the lamination bore radius (therefore, the small arc surface needs to be taken into account in the slot surface calculation).
The yoke surface is defined as the cylinder between the slot bottom radius and the radius of the lamination which is not the bore radius (Rext for external lamination).
The teeth surface (and therefore the teeth) is defined as the remaining surface between the bore radius and the slot bottom radius.
Slot geometry convention (external lamination):
Slot geometry convention (internal lamination):
The opening angle of the slot is the angle of the arc formed by the first and last points of the slot along the lamination bore radius, with O=(0,0) as the center.
The active surface of a slot is a closed surface meant to receive a winding or a magnet.
The equivalent active angle is the angle of the equivalent polar geometry of the slot active surface. This equivalent polar geometry is defined assuming the same (polar) height as the real active surface. The angle being such as the equivalent polar area equals the real active surface area.
The active height is defined as the difference between the slot bottom radius and the radius of the closest active surface point from the lamination bore.
The opening height is defined as the difference between the radius of the closest active surface point from the lamination bore and the lamination bore radius.
The mid-active radius is defined as the slot top radius minus half the active height for external lamination, or as the slot top radius plus half the active height for internal lamination.
Several of these methods use polar definitions for the height or for the angle to be able to easily define a polar equivalent of the machine (for instance for subdomain model – Magnetic module). It also enables to define the numerical methods in the Slot class which enables to skip the definition of these methods in the daughters classes (in particular for SlotUD/SlotUD2).
All the Slot objects have the following methods:
_comp_coordinates(): (optional) Returns a dict of the complex point coordinates of the slot (Key = “Zx”)
_comp_line_dict(): (optinal) Returns a dict of the main lines to draw the slot (key: “X-Y” = line begin=Zx, end=Zy)
build_geometry(): Returns a list of Line objects that enables to draw in 2D a single slot centered on Ox with lines ordered in trigonometric direction (no bore arc, the beginning of each Line is the end of the previous one).
build_geometry_active(): Returns a list of Surface objects that enables to draw in 2D the active surface (taking 2 integer, Nrad and Ntan, to split the original surface).
check(): Checks that all the geometrical constraints are respected, throw exceptions otherwise.
comp_angle_opening(): Returns the opening angle of the slot.
comp_angle_active_eq(): Returns the equivalent angle of the active surface of the slot.
comp_height(): Returns the slot’s height.
comp_height_active(): Computes the active surface height.
comp_surface(): Computes the surface of a single slot.
comp_surface_active(): Computes the active surface of a single slot.
comp_radius_mid_active(): Computes the mid radius of the active surface.



